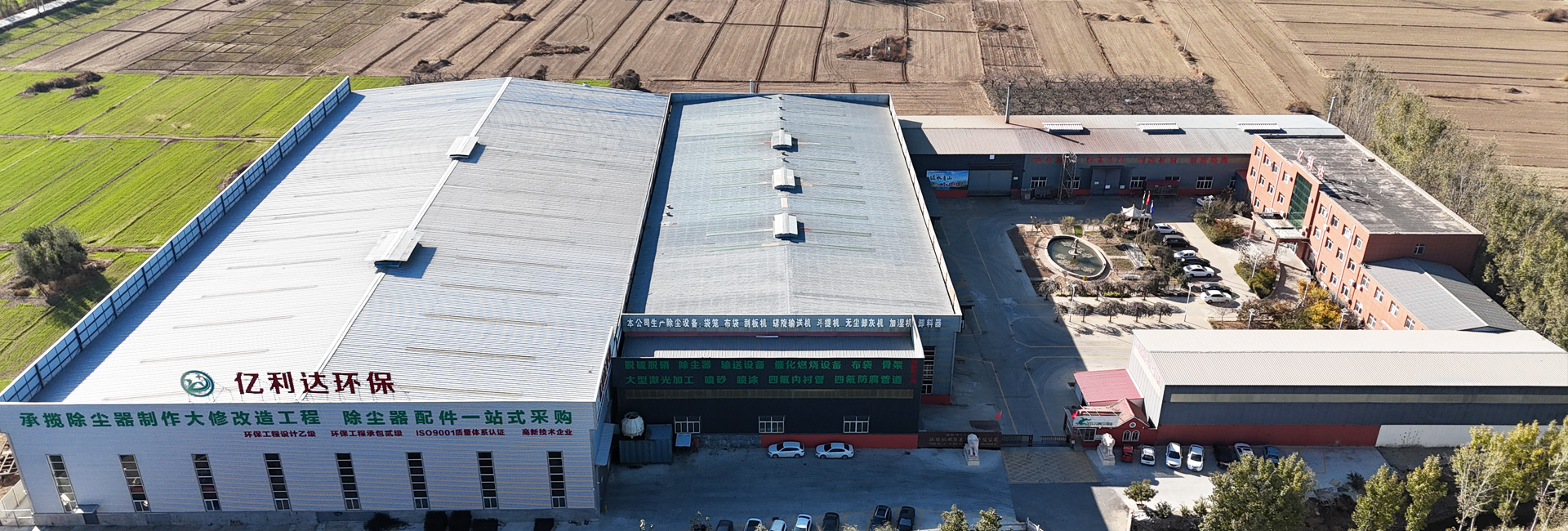
-
All
-
bag Dust Collector
-
Electrostatic Precipitator
-
Cartridge Dust Collector
-
Desulfurization And Denitrification Equipment
-
Dust Collector Bag
-
Dust Collector Skeleton
-
Electromagnetic Pulse Valve
-
Rotary Valve
-
Screw Conveyor
-
Dust Conditioner
-
Plug Valve/Butterfly Valve
-
Scraper Conveyor
-
Catalytic Oxidizer
-
Cyclone Dust Collector
-
Sintered Plate Dust Collector
-
Spray Tower
-
Activated Carbon Adsorber
-
Light Oxygen Purifier
-
Dry Filter Box
-
Bucket Elevator
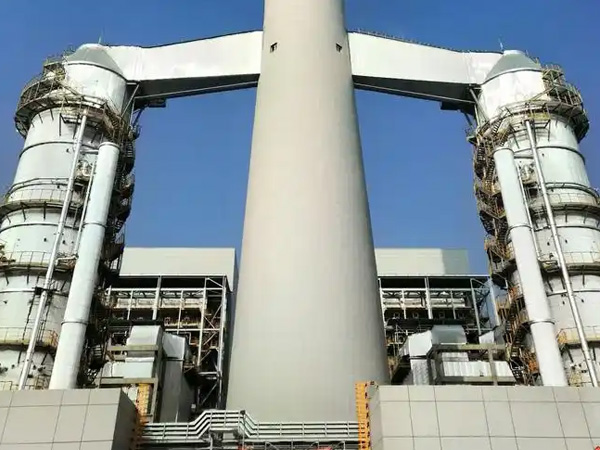

Ammonia-based Flue Gas Desulfurization
Ammonia-based Flue Gas Desulfurization (Ammonia-based Flue Gas Desulfurization, referred to as Ammonia FGD) is a desulfurization technology that uses ammonia (ammonia, liquid ammoni...
Ammonia-based Flue Gas Desulfurization (Ammonia-based Flue Gas Desulfurization, referred to as Ammonia FGD) is a desulfurization technology that uses ammonia (ammonia, liquid ammonia or ammonium bicarbonate, etc.) as a desulfurization agent, and the core converts useless SO₂ into high-value ammonium salt products (such as ammonium sulfate) through the chemical reaction between ammonia and sulfur dioxide (SO₂) in flue gas, which has the advantages of good desulfurization efficiency, no risk of solid waste accumulation, and product recycling, and is widely used in chemical industry and electric power , metallurgy and other industrial industries, especially suitable for surrounding fertilizer needs or convenient ammonia sources.
1. Core principle: chemical reaction mechanism
The essence of ammonia desulfurization is the neutralization reaction between acid gas (SO₂) and alkaline desulfurizer (ammonia), the whole process is carried out in aqueous solution, the reaction speed is suitable, the selectivity is strong, and the core reaction is divided into two steps: "absorption" and "oxidation":
SO₂ absorption reaction: SO₂ in flue gas enters the absorption tower first, contacts with aqueous ammonia solution and dissolves at an appropriate speed to form ammonium sulfite or ammonium bisulfite (the reaction product is adjusted with the degree of ammonia excess):
In case of excessive ammonia: SO₂+2NH₃・H₂O→(NH₄)₂SO₃+H₂O
When ammonia is insufficient: SO₂+NH₃・H₂O→NH₄HSO₃
To ensure adequate absorption of SO₂, the process usually controls the excess ammonia to produce ammonium sulfite, which is more stable.
Oxidation reaction: In order to avoid the decomposition of ammonium sulfite and the release of SO₂ again, compressed air needs to be passed into the absorbent solution to oxidize ammonium sulfite into stable ammonium sulfate (final product):
2(NH₄)₂SO₃+O₂→2(NH₄)₂SO₄
The oxidation process needs to control the temperature (40~60°C) and pH value (6.5~7.5) to confirm the oxidation efficiency ≥ 90% and protect the purity of ammonium sulfate.
2. Mainstream process: ammonium sulfate method (most widely used)
In the ammonia desulfurization technology, the ammonia-ammonium sulfate method is the most mature process in industrial application at present, and the core is to convert the desulfurization product into ammonium sulfate fertilizer for agricultural use to achieve "waste control and resource utilization", and its process flow can be divided into five core systems, as follows:
Flue gas system: The original flue gas (including SO₂, dust, etc.) discharged from the boiler is first removed by the dust collector (electrodust removal or bag dust removal), and then cooled to 50~60°C by the flue gas heat exchanger (GGH) (which is conducive to SO₂ dissolution and ammonia absorption), and then enters the absorption tower.
Absorption system: The absorption tower is the core equipment (mostly counter-current spraying type), the top of the tower is sprayed with ammonia aqueous solution, and the flue gas moves well from below, and the two are fully contacted to complete SO₂ absorption; A mist eliminator is set up in the tower to remove the ammonia mist and droplets carried in the clean flue gas to avoid "ammonia escape" (the ammonia escape rate is usually controlled below 5mg/m³).
Preparation and supply of desulfurizer: If liquid ammonia is used, it needs to be converted into gaseous ammonia by a liquid ammonia evaporator, and then mixed with water to make ammonia with a concentration of 15%~20%; If ammonia or ammonium bicarbonate is used, it is diluted directly and pumped into the absorption tower.
Ammonium sulfate preparation system: absorb the ammonium sulfite solution at the bottom of the tower into the oxidation tower (or the oxidation area in the tower), and oxidize it into ammonium sulfate solution through compressed air; Subsequently, the ammonium sulfate solution is sent to the evaporation crystallizer, concentrated and crystallized by steam heating, and then separated by a centrifugal dehydrator, and the ammonium sulfate crystals with a moisture content ≤ 1%. After that, it is dried and packaged to make a finished ammonium sulfate fertilizer (purity ≥90%).
Clean flue gas discharge system: After removing SO₂, the clean flue gas (SO₂ concentration ≤ 35mg/m³, meeting the ultra-low emission requirements) is heated to more than 80°C by GGH (to avoid chimney condensation corrosion), and finally discharged through the chimney.