-
All
-
bag Dust Collector
-
Electrostatic Precipitator
-
Cartridge Dust Collector
-
Desulfurization And Denitrification Equipment
-
Dust Collector Bag
-
Dust Collector Skeleton
-
Electromagnetic Pulse Valve
-
Rotary Valve
-
Screw Conveyor
-
Dust Conditioner
-
Plug Valve/Butterfly Valve
-
Scraper Conveyor
-
Catalytic Oxidizer
-
Cyclone Dust Collector
-
Sintered Plate Dust Collector
-
Spray Tower
-
Activated Carbon Adsorber
-
Light Oxygen Purifier
-
Dry Filter Box
-
Bucket Elevator
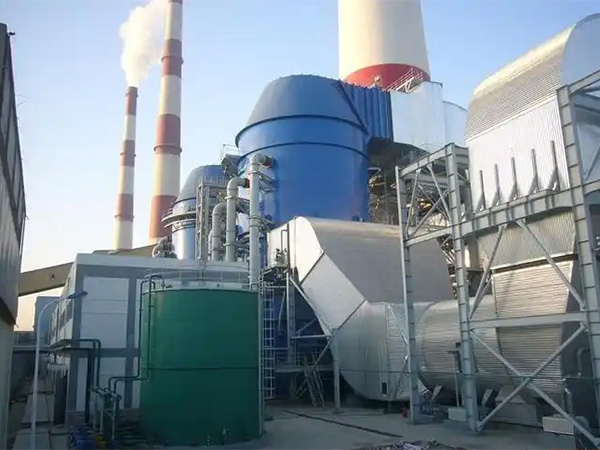

Flue Gas Denitrification Technology
Flue gas denitrification technology is an environmentally friendly technology that reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in combustion flue gas through physical and chemical method...
Flue gas denitrification technology is an environmentally friendly technology that reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in combustion flue gas through physical and chemical methods. It is mainly divided into two types: dry and wet processes, among which selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and selective non catalytic reduction (SNCR) are the mainstream dry processes in the building environment engineering industry. SCR technology utilizes catalysts to achieve 80% -90% denitrification efficiency in the temperature range of 320-400 ℃, but there is a risk of catalyst poisoning; SNCR technology achieves 30% -80% efficiency through high-temperature reaction at 850-1100 ℃, with lower cost but higher ammonia escape. The hybrid process combines the advantages of both and has engineering adaptability in terms of system optimization and equipment modification workload.
Mainstream process characteristics
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
Under the action of a catalyst, ammonia undergoes a reduction reaction with NOx to produce nitrogen gas and water. The typical reaction equation is: $4NO-4NH_3+O2rightarrow 4N2+6H2O. The core implementation elements include:
Catalyst selection: Metal oxides such as V2O5/TiO2 determine the reaction temperature window (280-420 ℃) and activity lifetime
System layout: High dust layout (between economizer and air preheater) can reduce renovation costs
Key technology: Flow field simulation optimization to confirm the uniformity of ammonia mixing, vortex mixer (VGM) to improve reaction efficiency
By 2025, SCR technology can extend the service life of catalysts to 3-5 years through ultrasonic vibration dust cleaning devices and waterproof (based on actual reports) toxic treatment processes.
Selective Non Catalytic Reduction (SNCR)
The denitrification reaction is completed in a high-temperature, catalyst free environment, and the main reaction mechanism is: Selective Non Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) technology achieves denitrification through a chemical reaction of ammonia water reducing NOx at high temperatures of 800-1250 ℃
Temperature window: The optimal reaction range is 850-1100 ℃, and the efficiency is improved by 15% -20% when urea is used as a reducing agent
System composition: including core components such as ammonia unloading system, storage tank area, and mixing distribution module
Space adaptability: Suitable for compact small and medium-sized boilers, with ammonia escape controlled below 4mg/Nm ³
SNCR/SCR hybrid process
Realize technological complementarity through process integration:
Stage 1: SNCR removes 30% -80% of NOx in the furnace
Phase 2: SCR treatment of residual pollutants, reducing catalyst usage by 50%
System advantages: The volume of the reaction tower is reduced by 30%, and the ammonia escape rate is controlled below 4mg/Nm ³